
Brownian motion in a smoke cell IOPSpark
The operations of averaging and taking the time derivative commute, so we can write the equation: m 2 d2 dt2 x2¯ ¯¯¯¯ + 3παη d dtx2¯ ¯¯¯¯ = KBT. (1.12.9) (1.12.9) m 2 d 2 d t 2 x 2 ¯ + 3 π α η d d t x 2 ¯ = K B T. To solve this differential equation, write d dtx2¯ ¯¯¯¯ = y. d d t x 2 ¯ = y. The equation becomes:

Brownian Motion setting up a Smoke Cell YouTube
Produced by the National STEM Learning Centre and Network and the Institute of Physics, this video illustrates how to show the movement of particles by Brown.

PPT Brownian Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3443530
An alternative: use a visualiser with a data projector and screen to enable students to observe Brownian motion in a suspension containing tiny polystyrene spheres. This experiment was safety-tested in March 2005. This video shows how Brownian motion can be observed in a suspension containing micrometre diameter polystyrene spheres.

Observing Brownian Motion with a Smoke Cell YouTube
Brownian motion refers to the random motions of small particles under thermal excitation in solution first described by Robert Brown (1827), 1 who with his microscope observed the random, jittery spatial motion of pollen grains in water. This phenomenon is intrinsically linked with diffusion. Diffusion is the macroscopic realization of the.

1.3 Diffusion & Brownian Motion Qatar Science
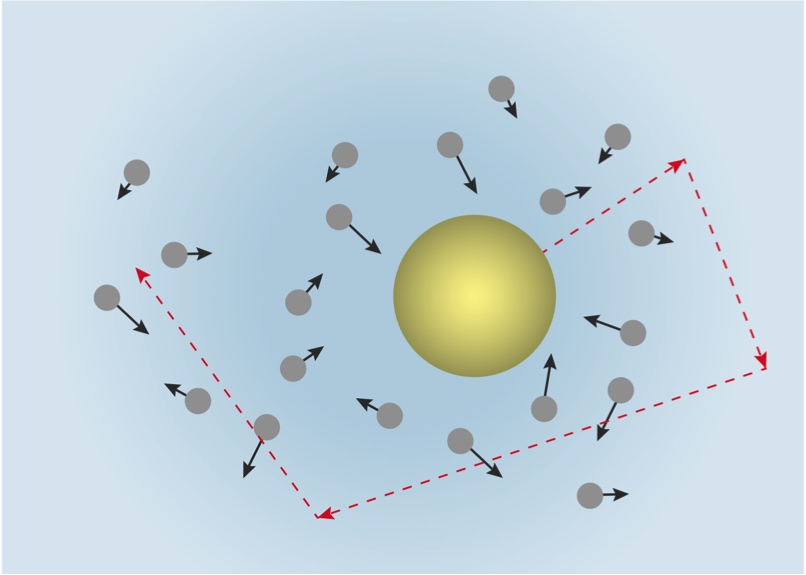
"Brownian motion refers to the random movement displayed by small particles that are suspended in fluids. It is commonly referred to as Brownian movement". This motion is a result of the collisions of the particles with other fast-moving particles in the fluid.

Brownian Motion IB Physics Mechanics KGV
Brownian Motion: Cool Experiments to Show How Particles Move in WaterBrownian motion is the random motion of particles suspended in a liquid or a gas. The mo.

PPT IDEAS ABOUT ATOMS PowerPoint Presentation ID5841704
1. Brownian Motion in Cells (current page) 2. Simulating Brownian Motion 3. Experimental Procedures 4. BMC Software This lab will be graded 30% on theory, 30% on technique, and 40% on analysis. For more information, see the Advanced Lab Syllabus. Comments: Submit feedback using this form. 2 The Brownian Motion in Cells Experiment Photos

30.1 Discovery of the Atom College Physics OpenStax
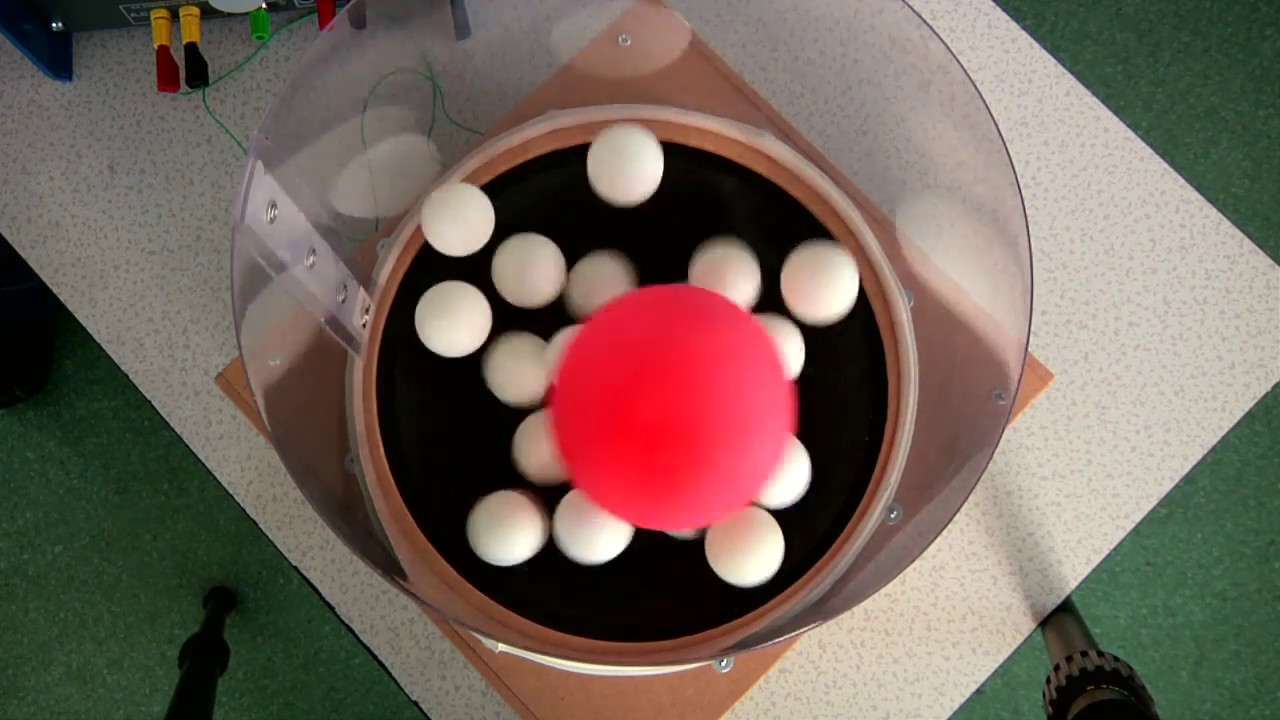
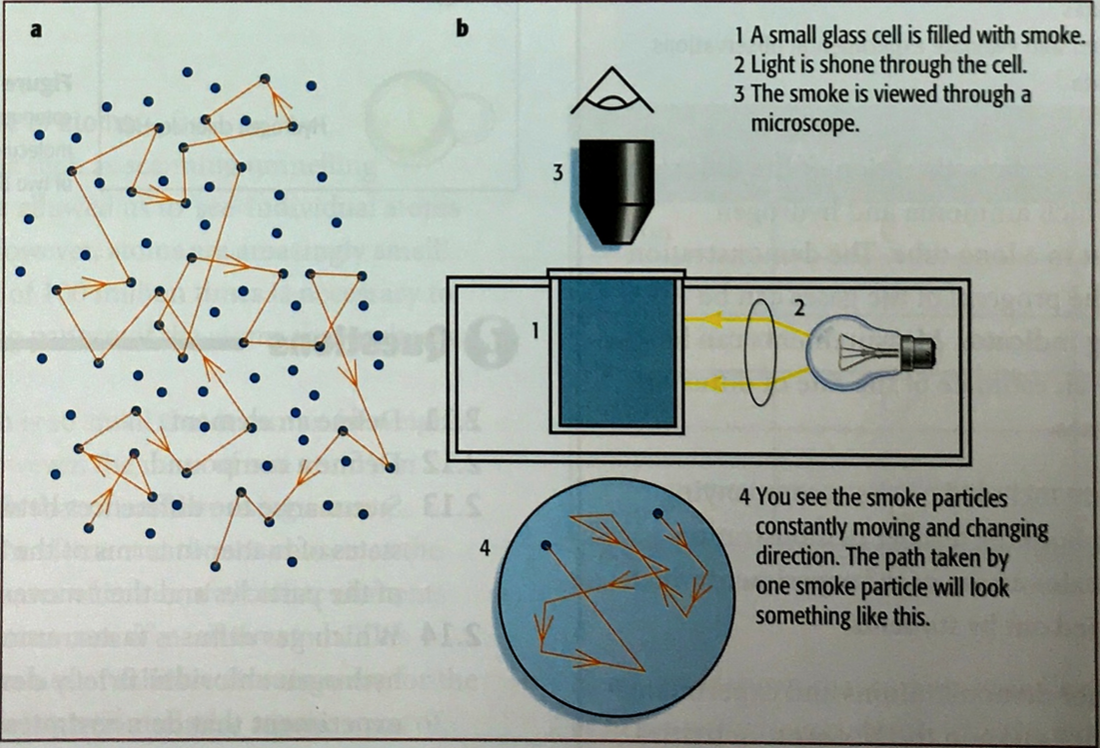
Well, one experiment which adds evidence to support this 'kinetic' theory is called 'Brownian Motion'. To set up this experiment, we need: a glass 'cell'. smoke from a glowing splint. a microscope with a light to illuminate the smoke particles. The smoke is trapped in the glass cell and the microscope is used to observe the motion of the smoke.
1.3 Diffusion & Brownian Motion Qatar Science
The goal of this experiment is to show real Brownian motion using a microscope. Theory In 1827, a Scottish botanist Robert Brown (1773-1857, Fig. 1) observed a chaotic motion of tiny particles ejected from pollen seeds suspended in water for the first time.

Researchers find the macroscopic Brownian motion phenomena of selfpowered liquid metal motors
Description of Albert Einstein's theory of Brownian motion and how he derived the size of atoms. © MinutePhysics ( A Britannica Publishing Partner ) Learn about Albert Einstein's theory of Brownian motion and how he derived the size of atoms based on how much the Brownian particles move

Brownian Motion science
Physics Pour food coloring in hot and cold water and see what happens. A simple but oh so important experiment about temperature and particles. Video Brownian motion Watch on Materials 2 drinking glasses Food coloring Water Step 1

What is Brownian Motion ? Physics
Brownian motion refers to the indefinitely continuing complex motion of particles, or granules, in a dilute emulsion or colloidal solution.Perrin's experiments were designed to yield theory-mediated measurements of aspects of that motion from features of it that could be observed in a sufficiently high-powered microscope.

Brownian Motion Easy Science Brownian motion, Interactive science notebook, Interactive science
Brownian motion is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium (a liquid or a gas ). [2] This motion pattern typically consists of random fluctuations in a particle's position inside a fluid sub-domain, followed by a relocation to another sub-domain. Each relocation is followed by more fluctuations within the new closed volume.
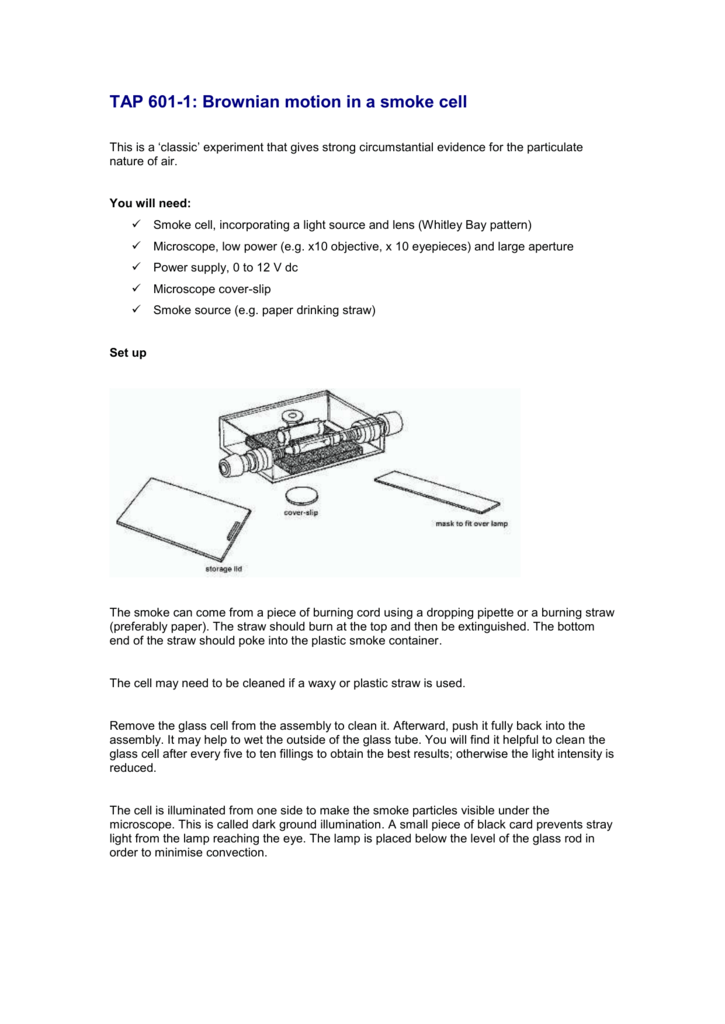
TAP 6011 Brownian motion in a smoke cell
Definition (#1.). A Brownian motion or Wiener process (Wt)t 0 is a real-valued stochastic process such that W0 = 0; Independent increments: the random variables Wv Wu, Wt Ws are independent whenever u v t (so the intervals (u;v), (s;t) are disjoint.)

A Level Physics Brownian Motion and the Smoke Cell Experiment YouTube
Brownian motion is considered a Gaussian process and a Markov process with continuous path occurring over continuous time. What Is Brownian Motion? Because the movements of atoms and molecules in a liquid and gas is random, over time, larger particles will disperse evenly throughout the medium.
Atom Archives Scott D. Bembenek
Brownian motion is the perpetual irregular motion exhibited by small particles immersed in a fluid. Such random motion of the particles is produced by statistical fluctuations in the collisions they suffer with the molecules of the surrounding fluid. Brownian motion of particles in a fluid (like milk particles in water) can be observed under a microscope. Here we describe a simple experimental.