CDN & SSL/TLS Faster Stronger Handshake CDN Guide Imperva
SSL/TLS Handshake: Ensuring Secure Online Interactions - SSL.com SSL/TLS Certificates Basic Premium High Assurance Enterprise EV Wildcard SSL/TLS Multi-domain UCC/SAN Enterprise EV UCC/SAN Smart SeaL Overview Code Signing Certificates Code Signing EV Code Signing Email, Client, and Document Signing Certificates Secure Email (S/MIME)
The Ultimate Guide to SSL/TLS Client Authentication Know How it Works
What Is the TLS 1.3 Handshake? TLS 1.3 eliminates several steps, reducing the round trips between client and server from two to just one by combining the client and server hello messages. The client sends a 'Client Hello' with its supported cipher suites and a random number. Instead of waiting for a server hello, the client sends its key share and predicted cipher and server certificate.
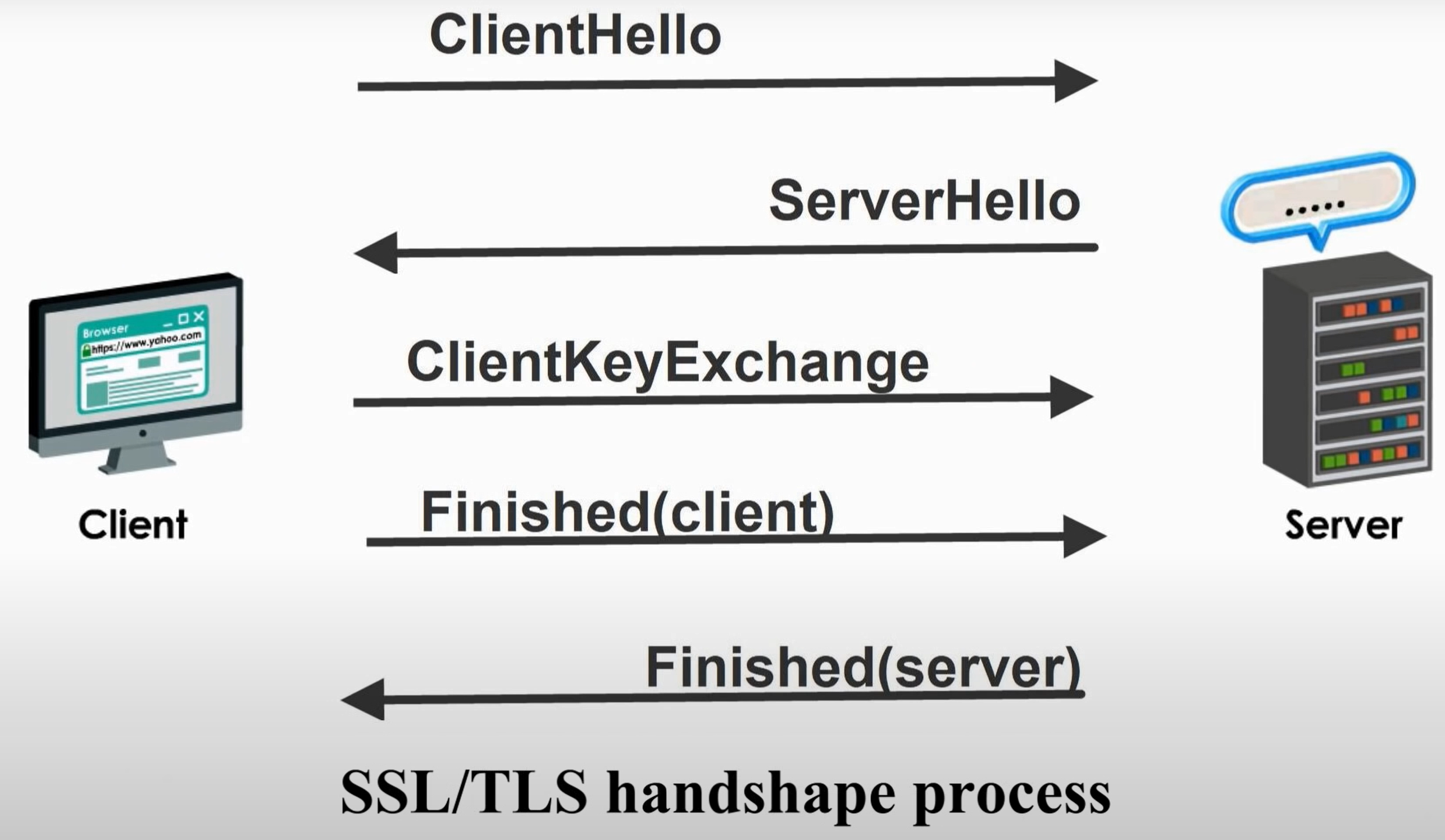
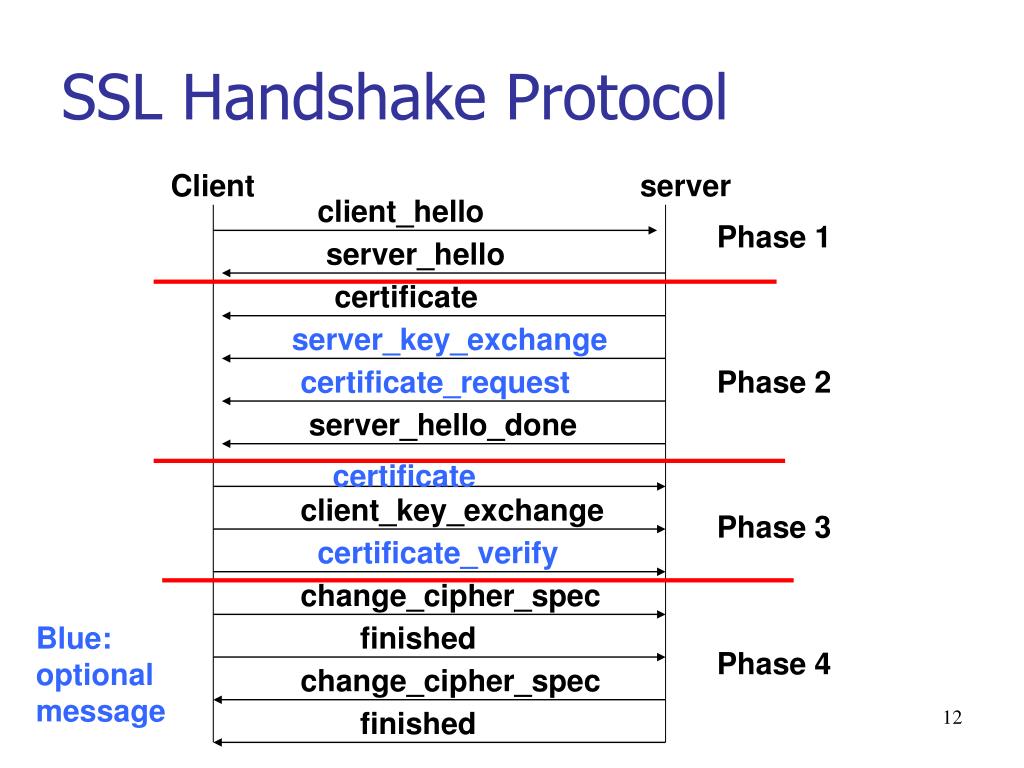
SSL/TLS Handshake Protocol Di Lin's Blog
What is SSL/TLS Handshake? SSL/TLS handshake is an arbitration made between the browser and the server for establishing the connection details. Since TLS replaced SSL before some time, all SSL handshakes are now defined as TLS handshakes. Both these parties decide on the below steps: TLS version which is to be used
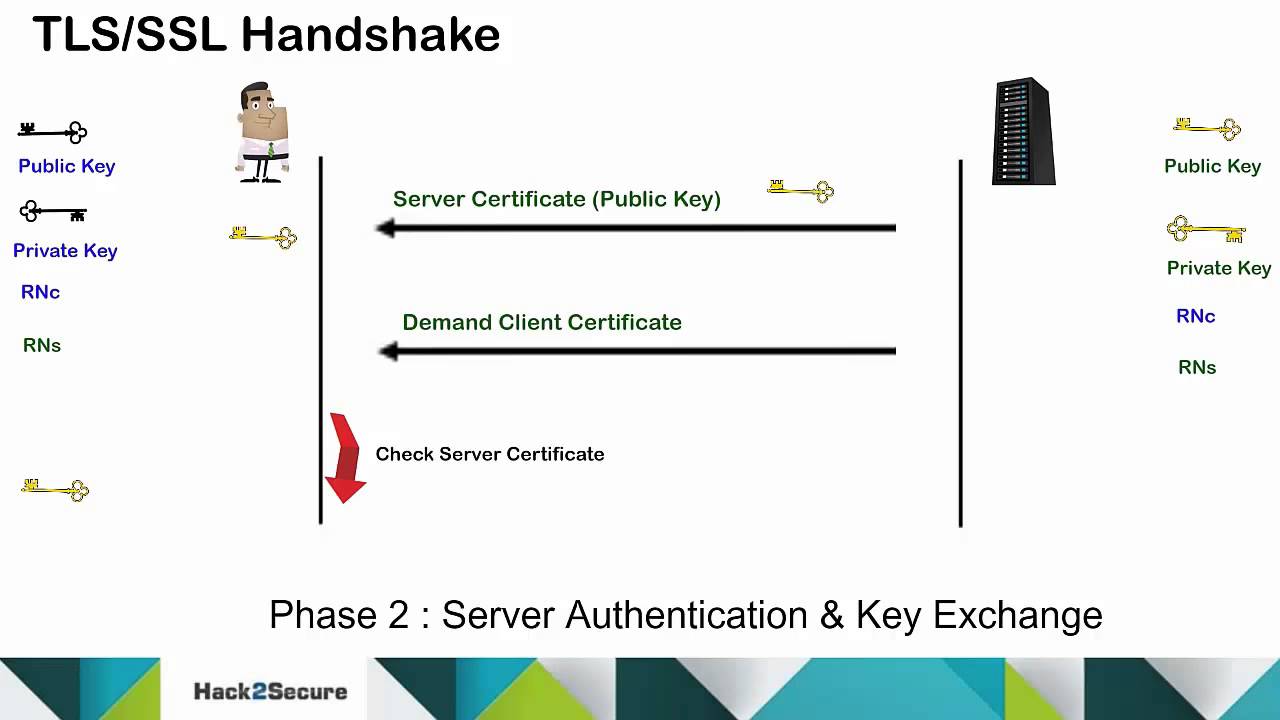
TLS/SSL Protocol and Handshake Process YouTube
A TLS encrypted connection is established between the web browser (client) with the server through a series of handshakes. In this article, I will explain the SSL/TLS handshake with Wireshark. HTTPS Connections Steps Client Hello Server Hello Server Key Exchange Client Key Exchange Change Cipher Spec Encrypted Handshake
What is TLS encryption and how does it work? Comparitech
The TLS Handshake Explained Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the cryptographic protocol behind pretty much any computer network used today: from web browsing to email, APIs, and VoIP. But how exactly does it work? Arthur Bellore Cybersec Writer March 07, 2023 SSL vs. TLS SSL, or Secure Sockets Layer, is the predecessor to TLS.
Tìm hiểu kiến thức cơ bản về SSL/TLS Handshake BKHOST
The Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol is the standard for enabling two networked applications or devices to exchange information privately and robustly. Applications that use TLS can choose their security parameters, which can have a substantial impact on the security and reliability of data.
What happens in a TLS handshake? SSL handshake Cloudflare
An SSL handshake defines a connection between two devices, such as your browser and the server that supports the website you want to visit. The word "SSL" in SSL handshake is a misnomer. The secure sockets layer (SSL) protocol is old, and people rarely use it these days. Now, most devices use transport layer security (TLS).

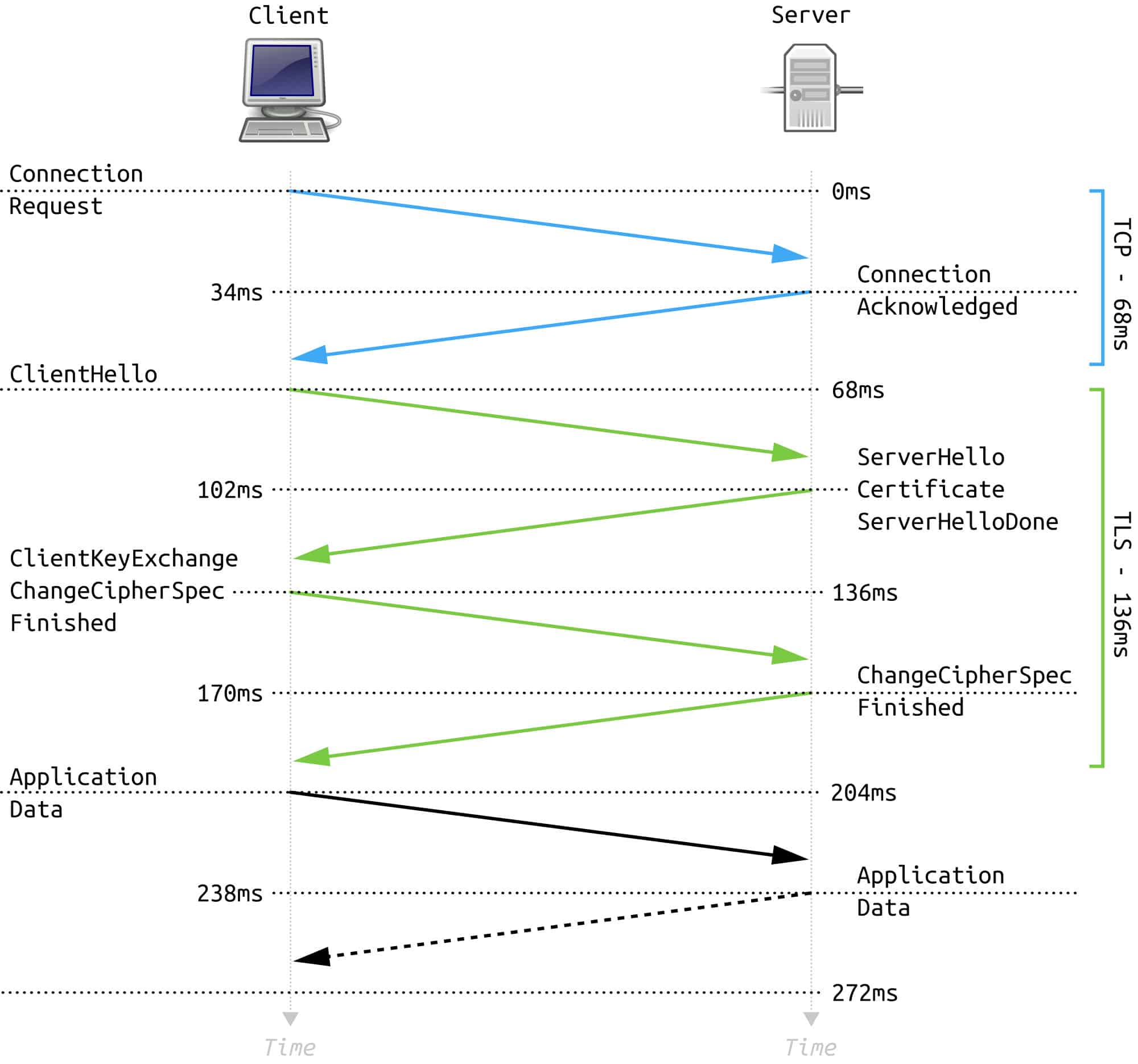
TLS handshake protocol Download Scientific Diagram
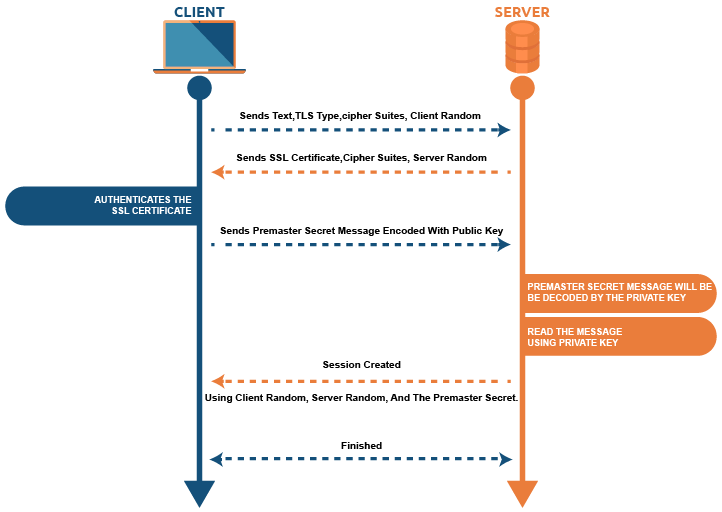
SSL/TLS handshake: Step by step. Based on the sort of key exchange method utilized and the cipher suites endorsed by both parties, the exact stages inside a TLS handshake can differ. The user starts the handshake process by sending a "Hello" message. This message contains the TLS type and cipher suites that the user supports.
SSL/TLS handshake the detailed process and how it works DevOps Technology Stack
The TLS (SSL) handshake is one layer of the TLS protocol, and its purpose is to authenticate the other party and establish secure parameters for the data exchange. The other major layer is the TLS record, which uses the parameters set up in the handshake to safely send the data between the parties. It transmits this data in packets called records.
The SSL/TLS Handshake Know the Process
An SSL handshake defines a connection between two devices, such as your browser and the server that supports the website you want to visit. During an SSL handshake, the two devices determine: What security version both parties will use What type of encryption will protect the information How both parties are verified

TLS (SSL) Handshakes Explained Online Security Protection
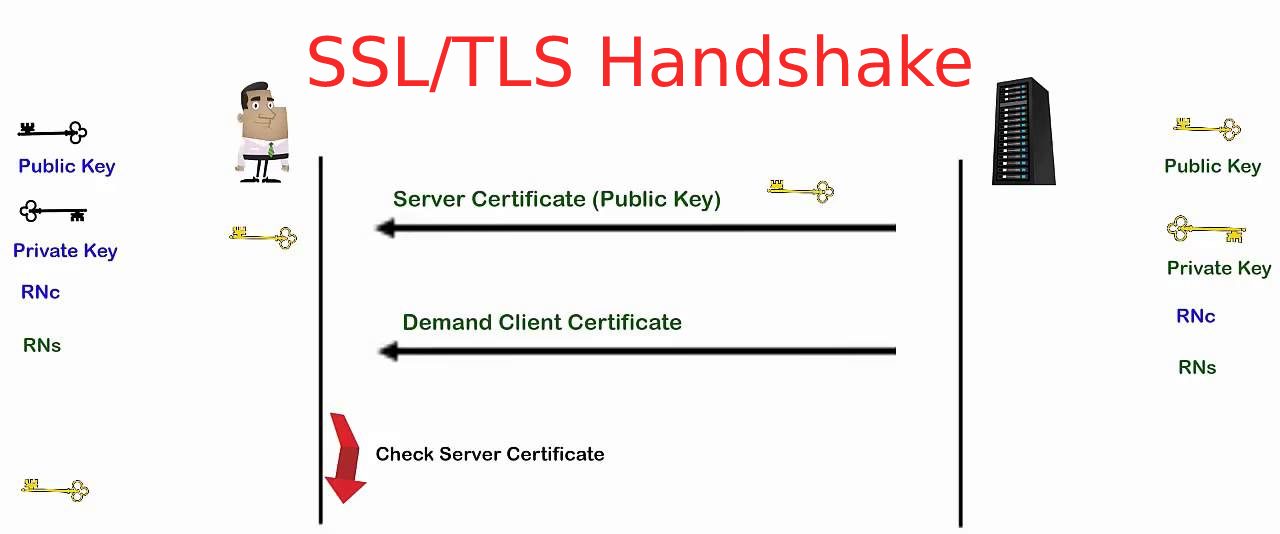
What is SSL/TLS Handshake? The SSL and TLS handshake establishes a system for SSL/TLS clients and servers to start communication between them in other words it is a negotiation between two parties on a network. Handshake Protocol is used to establish sessions.
PPT SSL/TLS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4370587
Obligatory SSL/TLS Handshake Graphic. All SSL/TLS-related sites have their own version of a handshake diagram - here's ours! (Click to enbiggen.) Let's Clear Up Some Confusion, If We Can. Some confusion about how SSL/TLS handshakes work is due to the handshake being only the prelude to the actual, secured session itself. Let's try to.

What is HTTPS The Definitive Guide to How HTTPS Works
The main purpose of an SSL handshake is to provide privacy and data integrity for communication between a server and a client. During the Handshake, the server and client will exchange important information required to establish a secure connection. There are two types of SSL handshakes described as one-way SSL and two-way SSL (Mutual SSL).
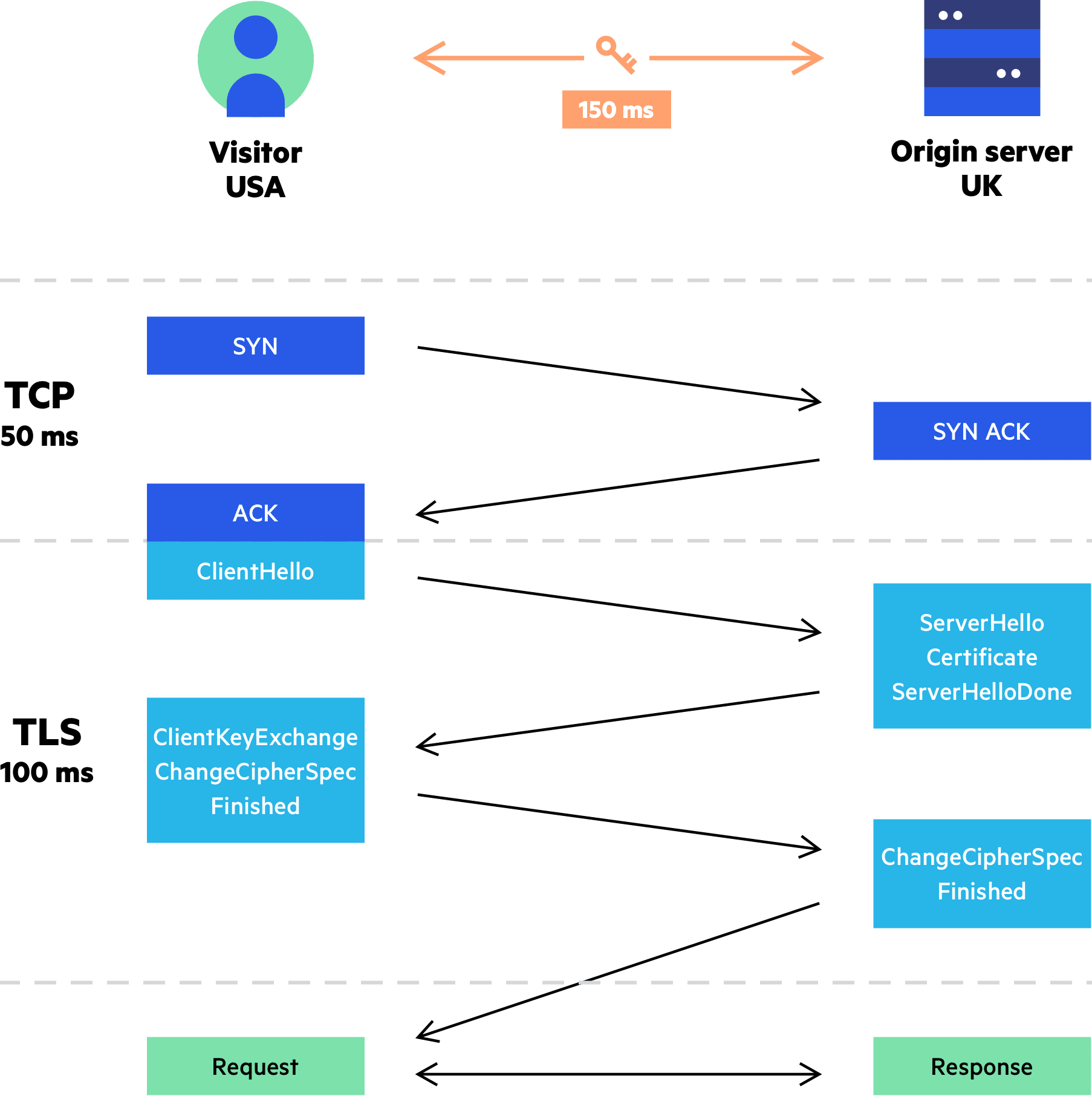
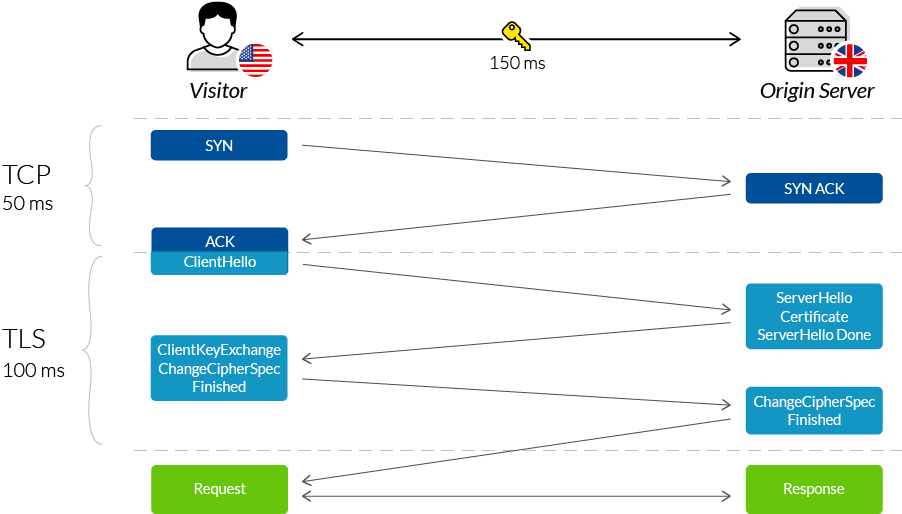
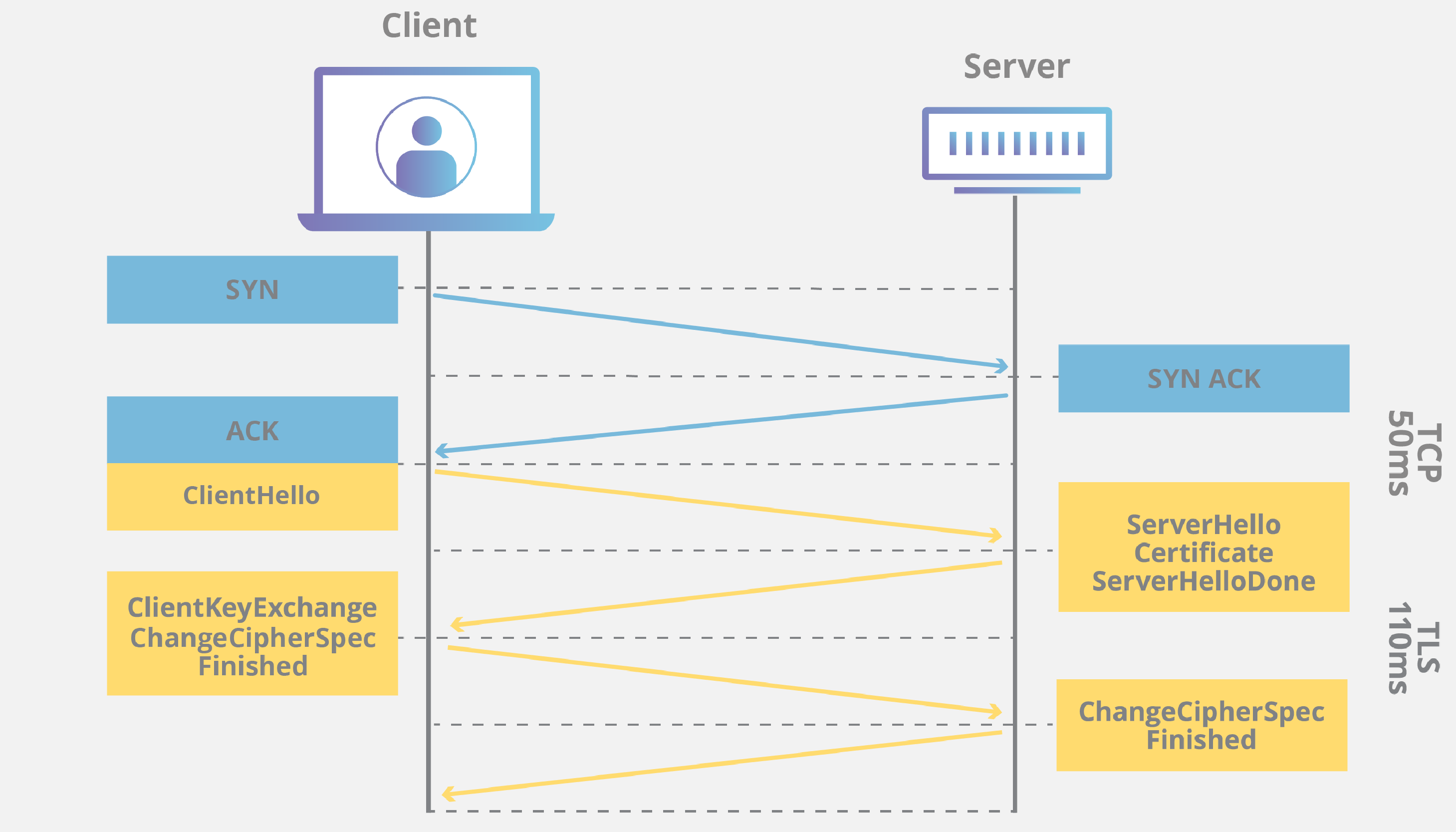
Imperva CDN Guide The Overhead of SSL/TLS Handshake
The simple way of looking at the SSL/TLS handshake is that it's a communication process that enables two parties to communicate securely on the internet. This is done by enabling the use of the secure hypertext transfer protocol (HTTPS) (instead of relying on the insecure traditional HTTP) by forming a TLS connection.
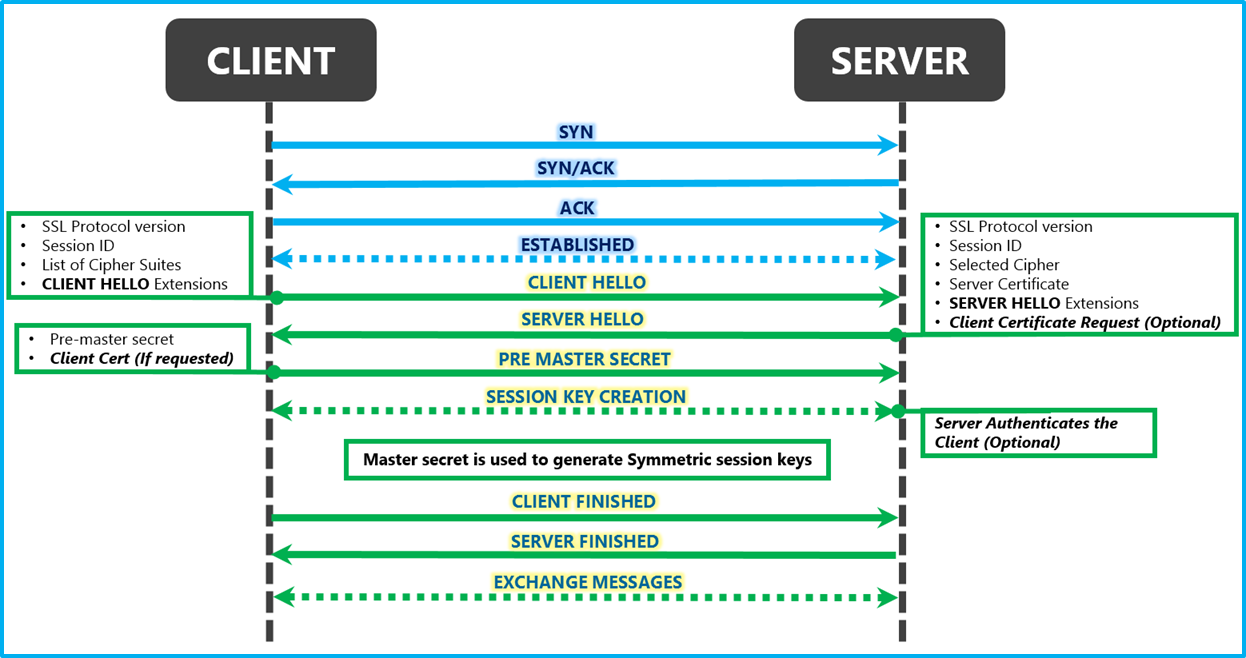
An overview of the SSL Handshake Robert van Rijn Medium
The 'SSL/TLS handshake' is the technical name for the process that establishes an HTTPS connection. Most of the hard work involved in the SSL/TLS protocol is done here. It's a process that has evolved since the original SSL protocol was first created in 1996, with each new iteration becoming faster, with less overhead.
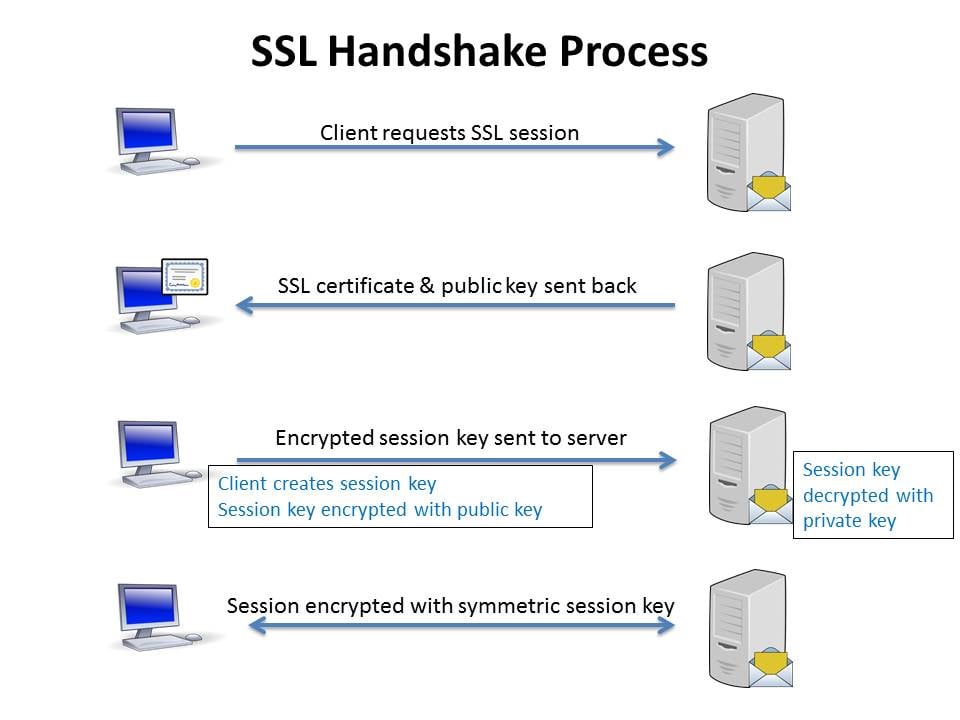
SSL & TLS Best Practices
The TLS Handshake, short for Transport Layer Security Handshake, serves as a protocol for initiating and establishing a secure connection between a client and a server, ensuring that the data exchanged between them remains confidential and tamper-proof. It has its roots in the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol, which was its predecessor.