
modulo Sterile chiuso earth cross section Medico invadere Petulanza
A vertical cross-section showing the trace of a geologic surface may be constructed in exactly the same way by noting where structure contours cross the line of section. Where a natural scale has been used and the line of section is perpendicular to the strike, the cross-section shows the true dip. On sections oblique to strike, the cross.
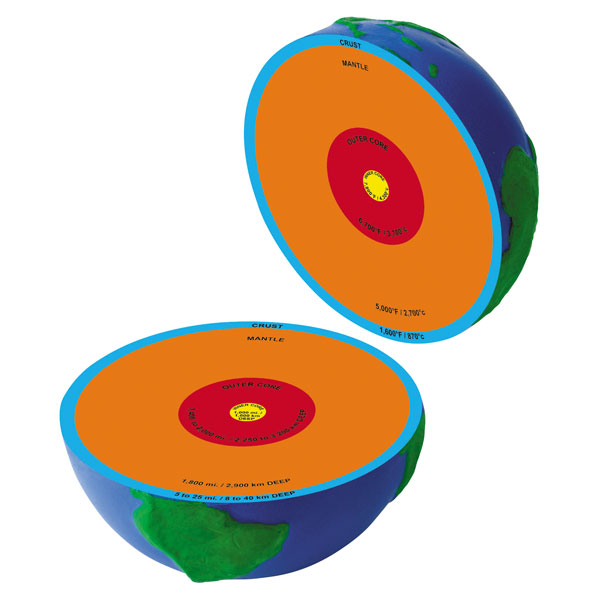
Learning Resources Cross Section Earth Model Rapid Online
The Cross section of the Earth is a visualization of the composition of the Earth in geological terms. The planet Earth is an immensely complicated and dynamic system, with many different physical and chemical properties. Most human experience of the Earth is limited to the surface however, with the deepest human endeavor made in 2012 to depths of 11 km in the Mariana's Trench.

Earth cross section, now 4,000 + views?! Information Graph… Flickr
A cross-section of the Earth, showing the sub-surface layers that are being mapped.

Earth Cross Section Diagram The Earth Images
A geological cross section is a diagram that displays geological relationships in a vertical plane extending into the Earth. Such diagrams present the appearance of exposing a slice of the Earth's interior to view. Cross-sections may be constructed entirely from either surface or subsurface data, or they may include both.

FileEarth cross sectioni18.png Wikimedia Commons
A cross-section of the Earth. March 17th 2017. "In every outthrust headland, in every curving beach, in every grain of sand there is a story of the earth.". - Rachel Carson (American zoologist), 1907-1964. We now know that the Earth is many billions of years old, and that it has changed an unimaginably number of times over millennia.

Earth Cross section 3D model CGTrader
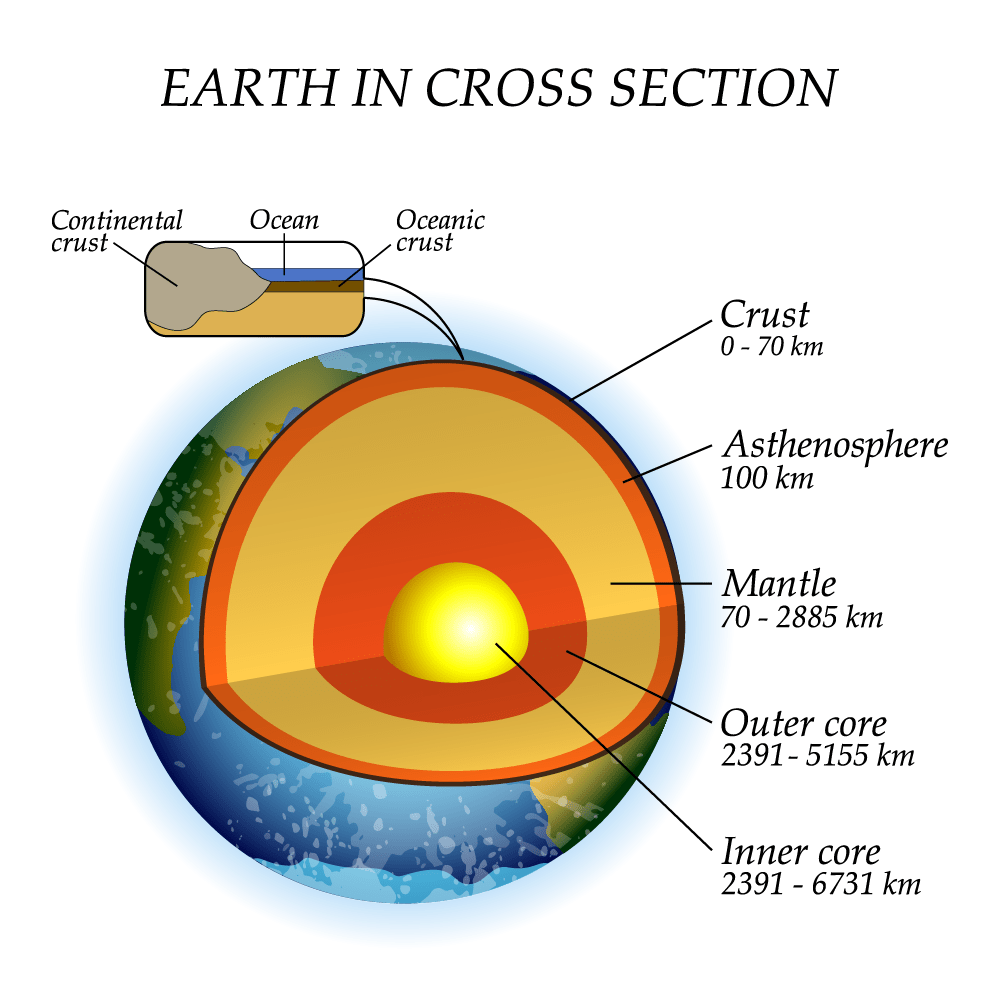
Geological cross section of Earth, showing its internal structure, the atmosphere and hydrosphere.. The internal structure of Earth is the layers of the Earth, excluding its atmosphere and hydrosphere.The structure consists of an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whose flow generates the Earth's magnetic field, and a solid inner core.

Earth World Cross Section · Free vector graphic on Pixabay
Figure copyright, A cross-section showing the Earth's structure. Which layer of the earth is closest to the surface? Show answer Hide answer. The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth.
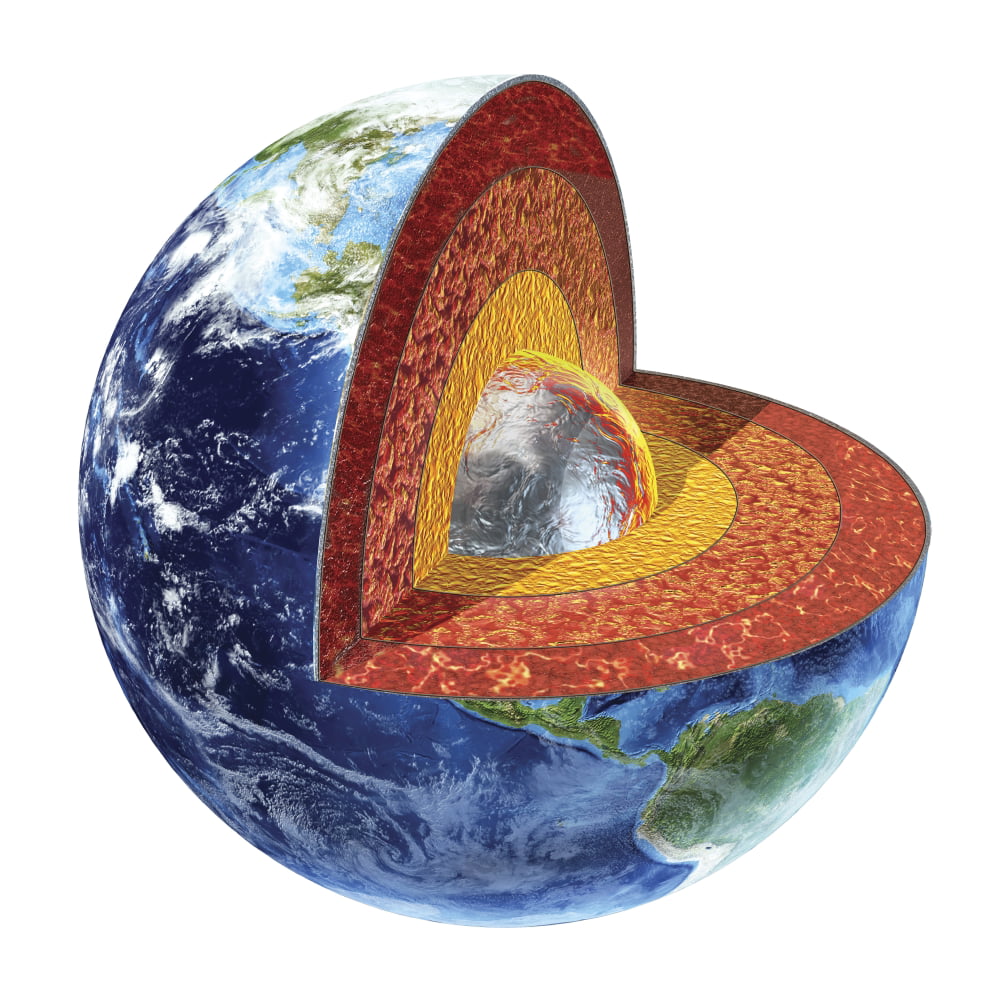
Cross section of Earth showing the inner core, made by solid iron and nickel, with a
Most geologic maps have the following features ( Figure 16.2 ): 1. The map itself. 2. The map legend or key that explains all the symbols on the map. 3. Geologic cross-section (s) of the map area. These will be explored further in the next chapter. Figure 16.2: 1) Geologic map, 2) legend and 3) cross-sections.

A crosssection through the Earth Highly Allochthonous
Figure 4.5: "Cross-section of Earth" (CC-BY 4.0; Chloe Branciforte and Cynthia Lampe, own work) This page titled 4.2: Activity 4A - The Structure of Internal Earth is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Chloe Branciforte & Emily Haddad ( ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative ) .

Cross Section Geology
Cross Section of the Earth. You may wish to print a copy of the lecture outline (minus the illustrations) and you have two options: Microsoft Word if you use that Word Processor or; A Netscape Document; that you can print (use the Left Arrow key to return to this page). Or, you may view the Earth's Interior power point presentation shown in class.
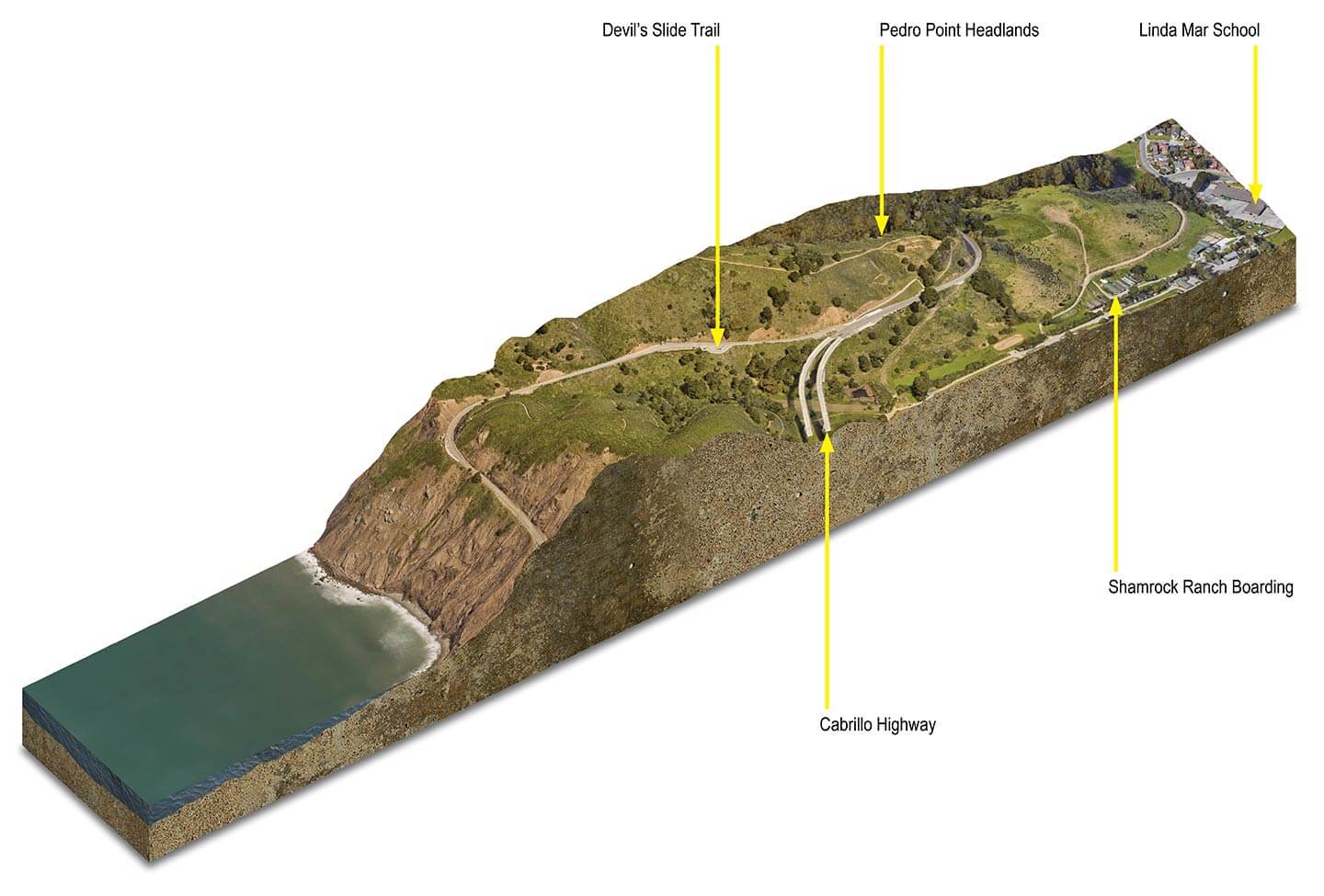
3D Cross Section Using Google Earth and Dylan Brown Designs
crust The thin layer that is the outermost section of the earth. It varies from between 5 - 70 km in depth and is broken up into several large pieces of rock which are known as plates. is the.

Earth Cross Section Diagram The Earth Images
Figure 2. Cross section of the whole Earth, showing the complexity of paths of earthquake waves. The paths curve because the different rock types found at different depths change the speed at which the waves travel. Solid lines marked P are compressional waves; dashed lines marked S are shear waves.

Earth Cross Section by Adam Dorman Digital Artist
The inner core is considered to be solid because of the behavior of P and S waves passing through it. Cross section of the whole Earth, showing the complexity of paths of earthquake waves. The paths curve because the different rock types found at different depths change the speed at which the waves travel. Solid lines marked P are compressional.
/wall-murals-earth-cross-section-lower-mantle-version.jpg.jpg)
Wall Mural Earth cross section. Lower Mantle version. PIXERS.US
Cross-section of the Earth (Let's Talk Science using an image by NASA [public domain] via Wikimedia Commons). Image - Text Version. Shown is a colour illustration of Earth's layers, shown as if the globe has been sliced to show the inside.
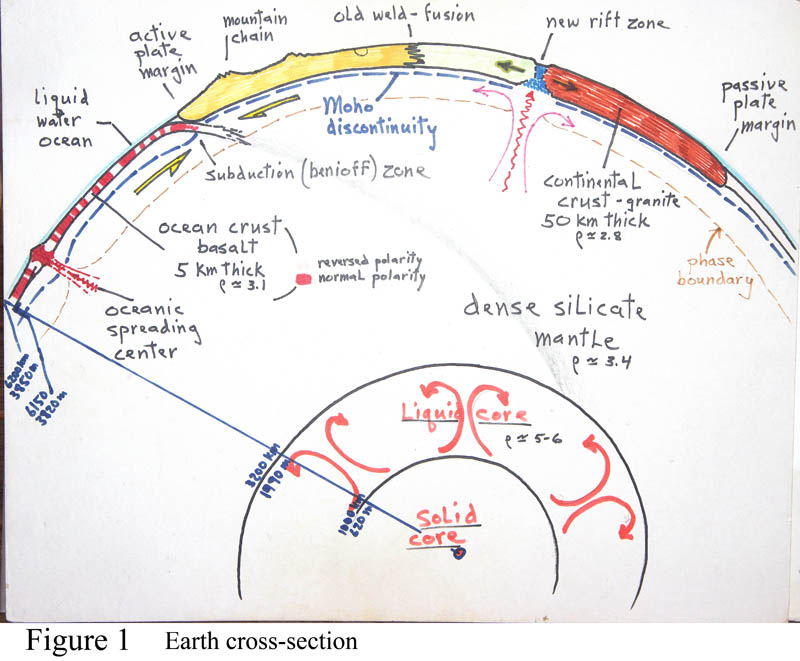
A crosssection of Earth, GEOLOGICAL HISTORY OF THE SOUTHWEST
Figure 1: A schematic diagram of the cross section of Earth showing its four internal layers. Earth's surface is known as the crust, and it is the thinnest and outermost layer of the planet.. Earth's crust can exceed 60 km in thickness and humans have only been able to drill 12 km into it. This means that most of the internal components.
Structure of the Earth Geography
Perspective view of Earth cross section. (Modified from figure on page 57 of Seismic Sleuths, FEMA/AGU.) Figure 4. Students constructing a "slice" of the Earth's interior at 1:10 million scale. Figure 5. Students constructing a "slice" of the Earth's interior at 1:10 million scale. Figure 6.